-
play_arrow
On The Street On The Air | Kaya 959
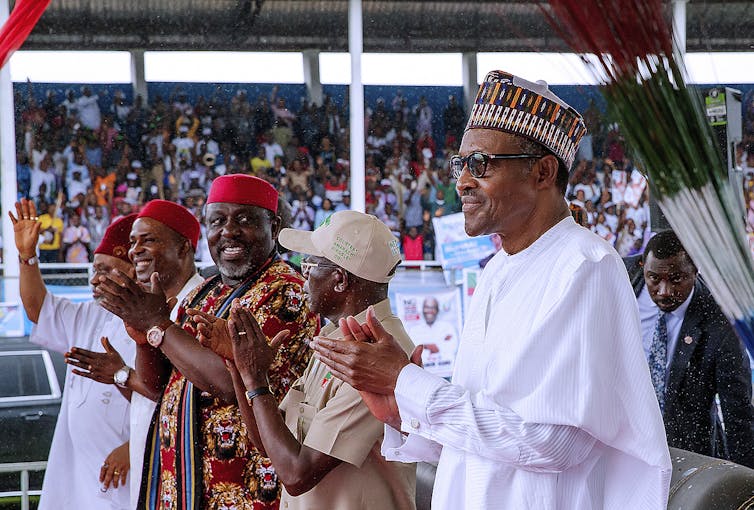
Nigeria has a history of dodgy elections: will it be different this time?
By: Ini Dele-Adedeji, SOAS, University of London

EPA-EFE/Stringer
Nigeria is preparing for its general election. But will it be credible? Nigerian voters are well aware that the elections will not be won solely by votes or popular consensus. There are several other variables that influence election results.
These include the incumbent’s control of state security apparatuses, grassroots structures, and control of institutions such as market traders associations, and the National Union for Road Transport Workers.
The road transport workers’ union, which acts as a canopy for bus drivers, conductors, and motor park touts in Southwestern Nigeria, has a history of providing foot soldiers for employment as election thugs with skills in ballot box snatching and voter intimidation tactics.
In addition, the possibility that the election could be rigged cannot be ignored.
Questions around the credibility of elections in post-independence Nigeria can be traced as far back as the “First Republic” which lasted from 1960 – 1966. After allegations of massive rigging in the 1965 elections the country’s western region was engulfed in the infamous “Operation Wet-ie” riots.
The riots pitted rival political groups against each other leading to Nigeria’s first military coup in 1966. From then on the country experienced a series of coups. Between 1966 and 1999, when the country made a decisive break with military politics, Nigeria experienced eight military coups. In that same time period three general elections were conducted.
Tumultuous past
The years outside of military rule were comparatively brief and arguably overshadowed by the spectre of the military. When elections did happen they were plagued by strong allegations of electoral fraud. Since 1999, when the country broke with military rule, five elections have been conducted all of which have been tainted by controversy.
It’s clear to see that Nigeria has survived a tumultuous political history. Going into this next election, questions still remain about the credibility of the country’s electoral system, and the viability of it’s governance structures. Looking back things have often gone wrong, but are there instances where things have worked out well for the electorate?
I would argue that there have at least two instances when voters got what they asked for. One is the June 1993 presidential election, which is considered to have been relatively free and fair in its conduct, its eventual annulment notwithstanding. Another is the presidential election of May 2015 when the incumbent Goodluck Jonathan, gracefully accepted defeat by conceding to President Muhammadu Buhari.
Yet I still feel that Nigeria’s electoral system needs a complete overhaul if it’s to perform its functions with as little external interference as possible.
Shadow of military rule
The country has been ruled by military administrators more than it has by democratically elected leaders. For 29 years of Nigeria’s independent history military dictators have had a grip on its leadership. This is compared to just 20 years of democracy. The result has been that electoral rigging and malpractice are rife within Nigeria’s electoral process.
Since 1999, Olusegun Obasanjo and Muhammadu Buhari, both of whom were previously military dictators spent a combined 12 years in power. President Buhari is now seeking a second term. As a result, there are still those who argue that the country’s transition from military rule to democracy is not quite complete.
The executive arm, for example, still maintains certain authoritarian characteristics that are reminiscent of the military era. One of these is the use of the armed forces to manipulate election processes. For instance, during the recent gubernatorial elections in Ekiti and Osun states voter intimidation by the security forces was rife. This was done to scare away opposition voters and give the ruling All Progressives Congress an edge.
The electoral commission
Another factor to consider is the supposed independence and impartiality of the Independent National Electoral Commission which is in charge of running the elections. Critics point to the fact that the commission chairperson and others in the commission are nominated by the president. This calls into question the credibility of the entire electoral commission.
Further, Buhari has just appointed Amina Zakari as the new collation officer. Zakari will oversee the committee responsible for the national collation centre from where results of the presidential election will be announced. But Zakari has been alleged to have a family relationship with the president. This has raised suspicion within opposition circles that the government intends to rig the polls.
To make matters worse, the behaviour of the electoral commission in previous elections hasn’t always been above reproach. This has lent credence to the criticisms bout the body’s impartiality. In the run up to the 2007 general for example, the Supreme Court ruled that the commission had no power to disqualify candidates in the eleventh hour as it had purported to do in the case of opposition candidate Atiku Abubakar.
The opaque nature in which recent gubernatorial elections have been held has also added to the fears of a rigged presidential poll. The September 2018 gubernatorial election in Osun, for example, was panned by election observers as being riddled with voting irregularities like voter harassment, and interference by “inappropriate persons”. These irregularities were reinforced by the high number of security officers deployed to the state during the election period.
The involvement of the security apparatus in tilting this tightly contested election in favour of the ruling All Progressives Congress is considered to be an indicator of how things could pan out in the general election.
Role of outsiders
Observers like the European Union and the US also exert a measure of influence on Nigerian elections. By ramping up the rhetoric on the importance of free and fair elections they play into the hands of the opposition who have historically appealed to foreign powers to umpire the electoral process.
Incumbent governments, on the other hand, have typically been on the other side of the argument. Nigerian governments have often cited what they call the “neo-imperialism” of countries like the UK and the US and decried their interference in Nigeria’s sovereignty. This resistance to foreign interference was most recently evidenced in comments made by Kaduna State governor, Nasir El-Rufai, who threatened foreign observers with death if they engaged with local politicians.
Former president Goodluck Jonathan also trotted out the “foreign interference” trope when he claimed in his recently published memoir that the US played a hand in ensuring that he lost the 2015 election.
And a few weeks ago the ruling All Progressives Congress joined the bandwagon when they issued a statement telling the EU to not undermine Nigeria’s sovereignty.
Not all grim
Despite all of the above, it’s not all grim. There are some positive precedents that can be built on.
For example, despite predictions that there would election violence during the 2015 poll, Jonathan did the honourable thing by conceding defeat to Buhari.
His concession reinforced the notion that elections need not be a “do or die” affair. This peaceful transition after just one presidential term in office also set a positive trend for elections across Africa.
But with the slim margin between the incumbent, Buhari, and his main contender Abubakar of the People’s Democratic Party – this narrative might need to be reinforced when Nigeria goes to the polls again on February 16.![]()
Ini Dele-Adedeji, Teaching Fellow, Politics & Development Studies, SOAS, University of London
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Written by: Natasha
Similar posts
-
MORE ARTICLES
-
QUICK LINKS
UpComing Shows

The Best T in the City
With T Bose
He has held it down in the world of mid-morning radio with the best music, riveting topics, brilliant mixes and interesting guests. Every weekday, The Best T proves why he is the BEST by connecting to you like only your bro or favourite uncle could. He lets his listeners dictate the songs they want to hear in the ever-popular Top 10 at 10, and his Three Teaspoons never run out. Catch The Best T in the City Mondays to Fridays from 09h00 to 12h00.
close
Feel Good
With Andy Maqondwana
Feel good about feeling good! That's exactly what The Feel-Good show is about. An escape from the negativity that surrounds us, indulging you in good feels. Pass it on to one and all. Spread the good feeling around Gauteng with Andy Maqondwana.
close
The Hive
With Bonolo "Bee Sting" Molosiwa
Every "Hive" needs a Queen B and Bonolo "Bee Sting" Molosiwa is Kaya 959's honey who brings in the money. With her bubbly personality, infectious laugh, Bee Sting radiates positive energy which is all you need to get your weekend off to the best start. Don't miss the Afrobeat Dancehall Ragga (ADR) Top 10 on The Hive with Bee Sting every Saturday from 18h00 - 21h00.
closeConnect with Kaya 959
DownLoad Our Mobile App
© 2024 Kaya 959 | On The Street On The Air